Why Profit Margin Erosion Matters in 2025
Profit margin erosion has become one of the most pressing risks in 2025. Companies across the USA, UK, UAE, France, and Asia are reporting tighter earnings ratios as CPI inflation, tariffs, and rising costs weigh on balance sheets. Finance professionals and policymakers are tracking these developments closely because shrinking margins signal both corporate stress and investor caution. Corporate profit decline is not only a business concern but also a signal of broader economic vulnerabilities.
Understanding the Profit Margin Squeeze
CPI Inflation and Corporate Earnings Pressures
CPI inflation impact is visible in almost every sector. Consumer prices continue to rise, but companies cannot fully pass costs to customers without hurting demand. This imbalance leads to operating margin risks. Input cost inflation in raw materials, logistics, and utilities is eating into revenue growth. The result is margin compression 2025 across developed economies. In the USA and UK, how CPI inflation erodes profit margins has become a priority for central banks monitoring inflation vs profits.
Tariffs and Global Trade Disruptions
Tariffs and profit squeeze are now linked directly. New U.S. and UK tariff policies are raising import costs, forcing companies to choose between reducing profits or raising prices. Many firms face supply chain cost inflation due to longer shipping routes and higher insurance costs. This has led to earnings losses 2025 in manufacturing and technology. For global markets, tariffs and input costs act as both inflation drivers and margin compression drivers.
Wage Growth, Input Costs, and Margin Compression
Wage inflation impact profits heavily in service and consumer sectors. Workers in high-income countries demand higher pay to keep pace with CPI inflation trends 2025. Companies in hospitality, retail, and healthcare find themselves squeezed between revenue stagnation and rising payroll costs. Earnings ratio analysis shows that labor-intensive businesses are facing the steepest decline in profit margins by sector. Wage inflation vs productivity remains unbalanced, which further intensifies global earnings slowdown.
Market Reactions to Profit Margin Erosion
Stock Market Volatility and Earnings Reports
Investors are reacting to corporate profit decline with caution. Earnings reports show frequent profit warnings, leading to stock market volatility.
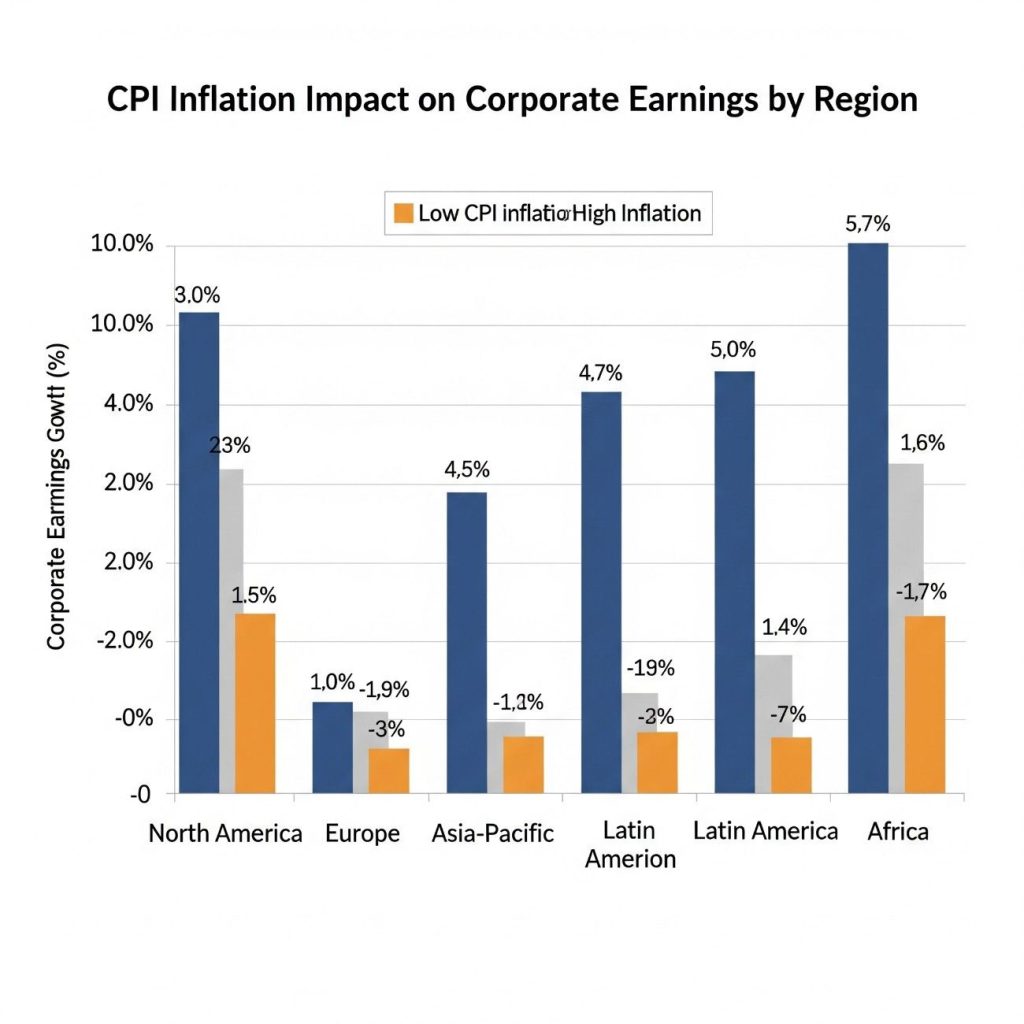
The relationship between inflation vs profits makes equities more sensitive to quarterly data. Market losses vs profits are being tracked closely in earnings seasons, as even small misses on margins lead to sharp stock price declines.
Sector-by-Sector Profit Risks
Profit margin decline trends in tech and energy sector stand out. Technology companies are pressured by higher semiconductor costs, while energy companies face volatile prices. Consumer goods firms report both falling volumes and reduced margins, despite higher sticker prices. Profit margins by sector reveal that luxury, healthcare, and defensive industries are holding up better, while manufacturing, logistics, and retail face stronger profit losses and earnings ratios deterioration.
Safe Haven Moves into Gold and Bonds
Safe haven flows are intensifying as investors hedge against profit margin erosion. Commodities like gold and U.S. Treasuries attract inflows. This reflects broader fears of earnings losses 2025. Institutional investors now balance equity allocations with commodities and fixed income to mitigate corporate profit decline.
Regional Earnings Trends in 2025
USA and UK: Inflation vs Profitability
In the USA and UK, CPI inflation and investor risk remain high. Rising tariffs increase supply chain costs, and many companies cannot offset them. How CPI inflation erodes profit margins in US and UK remains a core issue. Investors note that corporate profit decline could limit wage growth, slowing consumption and GDP expansion.
UAE and Gulf: Energy Profits Under Pressure
Profit losses and earnings ratios in UAE show energy companies are not immune. Although oil prices are relatively high, input cost inflation and geopolitical shocks on earnings disrupt stability. Energy profits under pressure reflect how regulatory costs on profits and OPEC+ policies create uncertainty.
Europe and France: Margins in Manufacturing and Luxury
France and broader Europe face margin compression 2025 in manufacturing. Energy costs remain elevated, and wage inflation is strong. However, luxury brands report resilience. Earnings ratio analysis highlights that luxury and premium goods show stronger pricing power compared with mass-market products.
Asia-Pacific: Tech and Consumer Goods Squeeze
Asia-Pacific economies, especially Japan, India, and China, face consumer sector margin compression. China’s CPI inflation trends 2025 remain moderate, but export tariffs raise costs. India’s consumer companies face wage inflation impact profits more visibly. Japan struggles with low pricing power and rising input costs, leading to operating margin risks.
Corporate Strategies to Manage Profit Margin Erosion
Passing Costs to Consumers vs Absorbing Losses
Firms balance between raising prices and absorbing cost inflation. Revenue vs cost growth dynamics show that aggressive price hikes reduce demand, while absorbing losses cuts profitability. Companies with strong brands can pass costs on, but smaller businesses suffer margin compression drivers without pricing flexibility.
Restructuring, Layoffs, and Cost-Cutting Moves
Restructuring is widespread. Companies cut staff and streamline supply chains to preserve margins. Layoffs reflect corporate profit decline, but also risk reducing productivity. Efficiency programs are central to controlling operating margin risks.
Shifting Supply Chains to Reduce Tariff Exposure
Tariffs and input costs push companies to relocate production. Shifting supply chains is expensive but necessary to reduce tariff exposure. Many multinationals diversify suppliers across Southeast Asia and India. This reflects the impact of tariffs on corporate earnings in 2025 and long-term strategic repositioning.
Investment Implications of Margin Compression
Risks for Equity Investors in 2025
Equity markets remain sensitive to profit margin erosion. Analysts expect earnings losses 2025 to weigh on valuations. Investors must review profit margins by sector and adjust portfolios accordingly. High-growth sectors face valuation pressure as CPI inflation impact cuts earnings expectations.
Commodities and Inflation Hedges
Gold, oil, and agricultural commodities remain key hedges. Commodities protect against CPI inflation and geopolitical shocks on earnings. They help balance equity losses in investor portfolios.
Opportunities in Defensive Sectors
Opportunities arise in healthcare, utilities, and consumer staples. These sectors show stronger resilience to margin compression 2025. Profit margin erosion is less severe because of steady demand and stronger pricing power.
Risks and Contradictions in the Earnings Outlook
Core Inflation vs Headline Decline
Headline inflation appears to be falling, but core inflation remains sticky. This mismatch confuses policymakers and investors. CPI inflation and investor risk continue as major factors in margin erosion forecasts.
For a deeper look at how the Qatar strike and the Ukraine war are reshaping Asia’s LNG and oil strategy, read our recent analysis on Energy Security in 2025.
Political and Regulatory Uncertainty
Regulatory costs on profits rise as governments impose new compliance standards. Political uncertainty from elections and trade negotiations adds volatility. These geopolitical shocks on earnings reduce investor confidence.
Energy Prices and Currency Volatility
Energy costs remain a wild card. Oil price swings influence corporate profit decline. Currency volatility in emerging markets adds further margin compression drivers for multinationals operating globally.
Regional Perspectives on Profit Margin Erosion
USA: Corporate Earnings and Tariff Shocks
U.S. companies see earnings ratio analysis show clear tariff impact. Supply chain cost inflation reduces profitability, while strong wage growth raises costs.
UK and EU: CPI Inflation and Weak Margins
UK and EU firms report profit losses and earnings ratios decline in key industries. CPI inflation impact on consumers limits pricing power, further cutting margins.
UAE and Middle East: Global Export Pressures
UAE exporters face input cost inflation due to supply disruptions. Profit margin erosion extends to both energy and non-oil industries.
Asia: Balancing Growth with Margin Compression
Asian economies face revenue vs cost growth imbalances. China, India, and Japan manage CPI inflation trends 2025 differently, but all report operating margin risks in consumer and tech industries.
Strategies for Policymakers and Investors
Strengthening Fiscal and Monetary Frameworks
Governments must stabilize inflation vs profits by aligning fiscal and monetary measures. Interest rates and targeted subsidies help balance CPI inflation impact.
Diversification of Investment Portfolios
Investors should diversify across geographies and asset classes. Commodities, defensive stocks, and alternative assets help counter profit margin erosion.
Preparing for Inflation and Earnings Shocks
Both investors and policymakers must prepare for shocks. Margin compression 2025 is a global issue requiring proactive strategy.
FAQs on Profit Margin Erosion 2025
How does CPI inflation affect profit margins?
CPI inflation impact reduces margins by raising costs faster than companies can raise prices.
What role do tariffs play in margin compression?
Tariffs increase supply chain cost inflation and reduce profitability across industries.
Which sectors are most exposed to earnings losses?
Tech, retail, manufacturing, and logistics face higher risks, while healthcare and utilities are more resilient.
How should investors respond to margin erosion?
Investors should hedge with commodities, diversify across defensive sectors, and monitor earnings losses 2025.
Conclusion: Positioning for Profit Margin Risks in Global Markets
Profit margin erosion in 2025 reflects how CPI inflation, tariffs, and input costs reshape global earnings. Investors, companies, and policymakers must adapt strategies quickly. Educational purposes only, not financial advice.