The Rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies 2025
Central bank digital currency is transforming the foundation of global finance. In 2025, more than 130 countries are exploring digital versions of national money. These new systems combine technology with monetary policy. They aim to improve efficiency, reduce risk, and strengthen financial inclusion.
The rise of CBDCs marks a shift toward programmable, traceable, and secure transactions. Governments are adopting them to modernize payment systems and reduce dependency on physical cash. For investors, CBDCs bring both opportunity and uncertainty. They change how capital flows, how policy is executed, and how markets react to monetary shifts.
Why Central Bank Digital Currencies Are Reshaping Global Finance
Central bank digital currencies change how money moves across economies. They allow faster settlements, lower transaction costs, and real-time tracking of liquidity. For example, China’s digital yuan and Europe’s digital euro projects show how public digital money can work at scale.
Moreover, CBDCs reduce intermediaries and improve transparency. They help regulators monitor illicit flows and make compliance stronger. As a result, they reshape traditional banking operations. However, this transformation also raises new risks that demand robust oversight.
The Link Between CBDCs and Monetary Stability
A well-designed central bank digital currency can strengthen monetary control. It gives central banks better visibility of money circulation. Therefore, policy transmission becomes faster and more precise. When implemented carefully, CBDCs can reduce volatility and inflation pressures.
However, poor design or rapid rollout may create instability. For example, if users shift deposits from commercial banks to CBDCs, liquidity could tighten. To avoid this, central banks are adopting tiered access and limits on individual holdings. In addition, many use pilot projects before mass deployment.
Regulation, Risk, and Data Protection Challenges
CBDC development also brings complex challenges in regulation and privacy. Governments must ensure user data is protected while maintaining traceability. Regulators are drafting global standards for interoperability and cybersecurity.
For example, the Bank for International Settlements and IMF coordinate on global CBDC frameworks. These efforts support secure, cross-border payments while reducing the risk of digital fraud. In conclusion, the balance between innovation and control defines the success of every CBDC program.
How Central Bank Digital Currencies Transform Global Financial Systems
The transition to central bank digital currency impacts all financial sectors. Banks must redesign settlement systems. Payment processors need to adapt to real-time transaction models. Fintech companies explore integrations that reduce fees and latency.
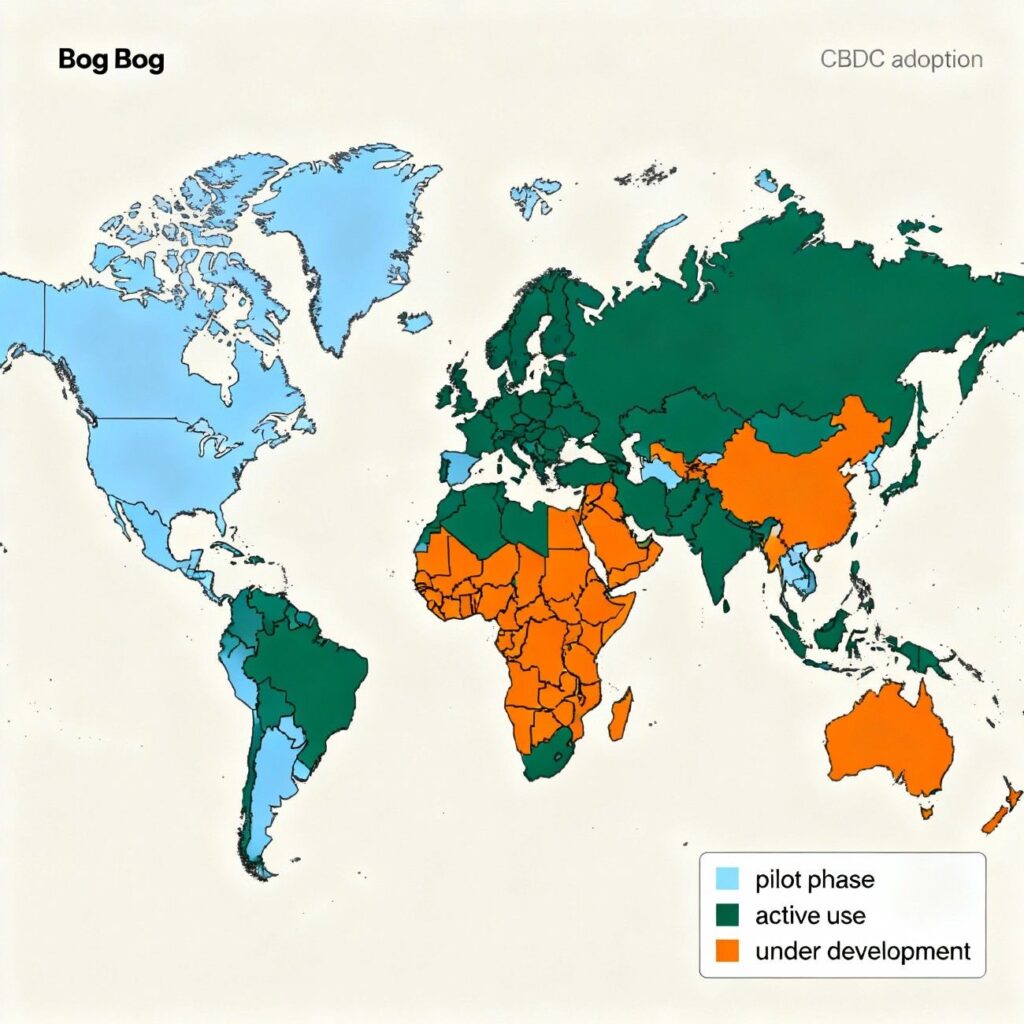
Moreover, CBDCs open new pathways for cross-border trade. Instant digital settlement can replace slow correspondent banking networks. This change improves trade efficiency and transparency. It also enhances economic integration among countries with shared digital standards.
The Role of Blockchain and AI in Central Bank Digital Currency Systems
Blockchain and artificial intelligence shape how CBDCs work. Blockchain ensures transparency and prevents double-spending. AI supports fraud detection, compliance, and transaction optimization. Together, they create a secure digital finance infrastructure.
For instance, Singapore’s Project Ubin and India’s digital rupee use distributed ledgers to test high-volume transaction reliability. These innovations reduce costs, speed up settlements, and promote trust. Furthermore, combining AI with blockchain improves system resilience against cyber threats.
Benefits for Banks, Fintechs, and Investors
CBDCs offer clear advantages for all stakeholders. Banks gain faster settlements and better liquidity management. Fintechs access regulated infrastructure for innovation. Investors gain transparency in financial flows and lower transaction costs.
As adoption grows, CBDCs can expand global liquidity. They also create new investment opportunities in digital infrastructure. However, proper regulation is essential to ensure fair competition and data protection.
Global Regulatory Landscape in Central Bank Digital Currency Finance 2025
Regulatory clarity remains a key factor for successful CBDC adoption. The Financial Stability Board and IMF lead initiatives to align rules among nations. Uniform standards prevent fragmentation and promote trust.
The European Central Bank, Federal Reserve, and People’s Bank of China share research on risk mitigation. Each region adopts its own model but aligns with shared goals. As a result, cross-border CBDC projects are gaining traction worldwide.
US, EU, and Asia Regulatory Developments
In the United States, the digital dollar project continues to evolve. In Europe, the digital euro enters its design phase. Across Asia, China, Japan, and India advance pilot testing with millions of users.
Furthermore, the UAE and Singapore lead in CBDC cooperation frameworks. Their goal is to improve remittance efficiency and trade finance. These regional examples show how coordinated policies accelerate progress.
The Role of BIS and IMF in CBDC Coordination
The Bank for International Settlements and IMF provide policy direction for CBDC networks. They coordinate interoperability among systems to prevent isolation. Consequently, they promote transparent governance and operational security.
These institutions emphasize resilience, data protection, and international collaboration. By guiding central banks, they ensure CBDC systems meet global standards.
CBDCs, Privacy, and Financial System Risks
CBDCs bring both transparency and privacy challenges. Every transaction can be tracked digitally. Therefore, balancing security with confidentiality becomes critical.
Central banks adopt layered privacy designs that protect user identity while allowing auditability. Moreover, multi-tier verification systems prevent misuse without exposing personal data.
Balancing Innovation and Financial Privacy
Maintaining privacy is vital to public trust. Without it, adoption slows. Governments must clarify how data is stored, who can access it, and under what conditions.
As a result, many nations introduce privacy-first frameworks. These include encryption standards, consent-based data sharing, and legal protection for users.
Mitigating Systemic and Cyber Risks
CBDCs depend on digital infrastructure, so cyber resilience is essential. Regulators enforce redundancy, encryption, and continuous monitoring. Furthermore, cooperation with private cybersecurity firms strengthens defense.
International testing by BIS Innovation Hub ensures readiness against major disruptions. These coordinated efforts help maintain financial stability.
Investment Opportunities in the Central Bank Digital Currency Era
Investors view CBDCs as a gateway to new opportunities. Digital infrastructure, payment platforms, and RegTech startups benefit most.
Moreover, financial institutions that adapt early can capture market share. As CBDCs mature, related sectors like cybersecurity and AI analytics will expand rapidly.
CBDC Infrastructure and Payment Networks
Modernizing payment infrastructure is at the center of CBDC growth. Governments fund upgrades in connectivity, blockchain systems, and authentication technologies.
Fintech companies partner with central banks to deploy scalable platforms. These collaborations create long-term business opportunities and attract institutional investors.
Strategic Risks and Market Implications
Although promising, CBDCs may disrupt existing markets. Commercial banks could lose deposits, and cross-border competition could intensify.
Therefore, proactive risk assessment is vital. Central banks implement gradual rollouts and liquidity safeguards to maintain confidence.
Regional Perspectives on Central Bank Digital Currency Adoption 2025
CBDC adoption varies across regions. China leads with the digital yuan. Europe follows with the digital euro, focusing on consumer privacy.
India and the UAE collaborate on pilot projects for real-time cross-border payments. Africa’s Nigeria introduces the eNaira, improving inclusion for the unbanked population.
Future Outlook for Central Bank Digital Currencies
The next phase of CBDC growth involves AI, blockchain, and decentralized finance integration. These technologies enhance interoperability and scalability.

Therefore, the financial system moves closer to a fully digital ecosystem. Policymakers must ensure fairness, transparency, and inclusiveness in this transition.
Common Questions About Central Bank Digital Currencies 2025
How will CBDCs affect global finance? They will make payments faster, cheaper, and more secure.
What are the main risks for investors? Technology failures, regulatory uncertainty, and liquidity shifts remain major concerns.
Which countries lead in CBDC development? China, India, the EU, and the US are among the leaders.
How can investors prepare for the CBDC era? They can explore fintech stocks, digital infrastructure firms, and blockchain investments.
Final Thoughts: Central Bank Digital Currencies 2025 and the Future of Global Finance
Central bank digital currencies will redefine financial systems in 2025 and beyond. Their success depends on trust, regulation, and international coordination.
CBDCs represent the next step in the evolution of money. They enhance inclusion, efficiency, and control while reshaping the role of central banks.
Educational purposes only, not financial advice.
